Treatment Options for UTI
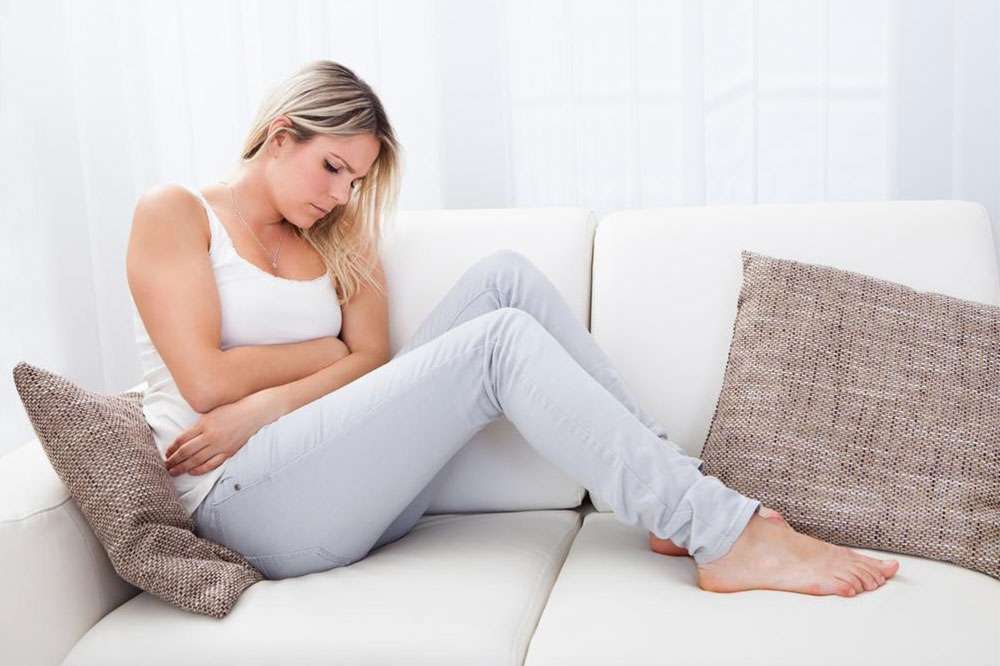
A urinary tract infection is usually accompanied by several indications. Generally, as soon as you approach a physician with the problem, a urine test (culture test) will be prescribed. The urine test will tell you about the bacteria you are dealing with. Furthermore, while antibiotics are the first line of treatments for UTI, the ideal approach will be decided based on the extent and severity of the infection. Here are the best treatment options for a this condition.
Simple Infection
Mild infections will clear up quickly (almost within a week) with a dose of antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed medicines in the treatments for UTI are
- Ceftriaxone
- Nitrofurantoine (Macrobid, Macrodantin)
- Trimethoprim, Sulfamethoxazole (Septra, Bactrim, etc.)
- Fosfomycin (Monurol)
- Cephalexin (Keflex)
Furthermore, depending on the kind of infection and your response to earlier infections/treatments, the doctor may prescribe a set of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones. These medicines are not the first option in the treatments for UTI. But if the infection is a complicated one or the kidneys, the doctor may prescribe these medicines. The entire antibiotics course must be completed even after the infection has subsided.
Moderate or Frequent Infection
There are situations wherein it can seem like one is struggling with a UTI more often than not. In such cases, the doctors may prescribe
- A low-dose of antibiotics will be prescribed and must be taken for a longer period. The duration will be dependent on the infection and your medical history. Generally, doctors prescribe such medication for 4-6 months. On review, such medication may even be extended beyond six months.
- If the infection is sexually transmitted, then treatments for UTI are almost similar. Cystitis or infection in the bladder is treated with a single dose of antibiotics to be taken immediately post intercourse.
- Small and minor infections may be diagnosed by the patient. Consultation, as agreed upon between the doctor and patient, may be used to arrive at suitable treatments for UTI.
- UTIs are commonly seen in post-menopausal women. Typically, estrogen production nosedives after menopause. Antibiotic resistance and the need to explore other options have given rise to Estrogen Therapy. This therapy involves vaginally delivering estrogen, which helps in reducing the occurrence of UTI in such cases. Doctors may prescribe this therapy as a preventive measure in patients who have recurrent UTIs in the post-menopausal stage.
Severe Infection
Generally, a severe infection will require a heavier and stronger dose of antibiotics.
- Depending on the infection’s severity, doctors may require patients to undergo treatment in a hospital.
- The antibiotics will be administered through intravenous injections.
It’s important to seek the advice of a physician as soon as the UTI symptoms present themselves. Timely treatments for UTI can prevent the worsening of the condition.